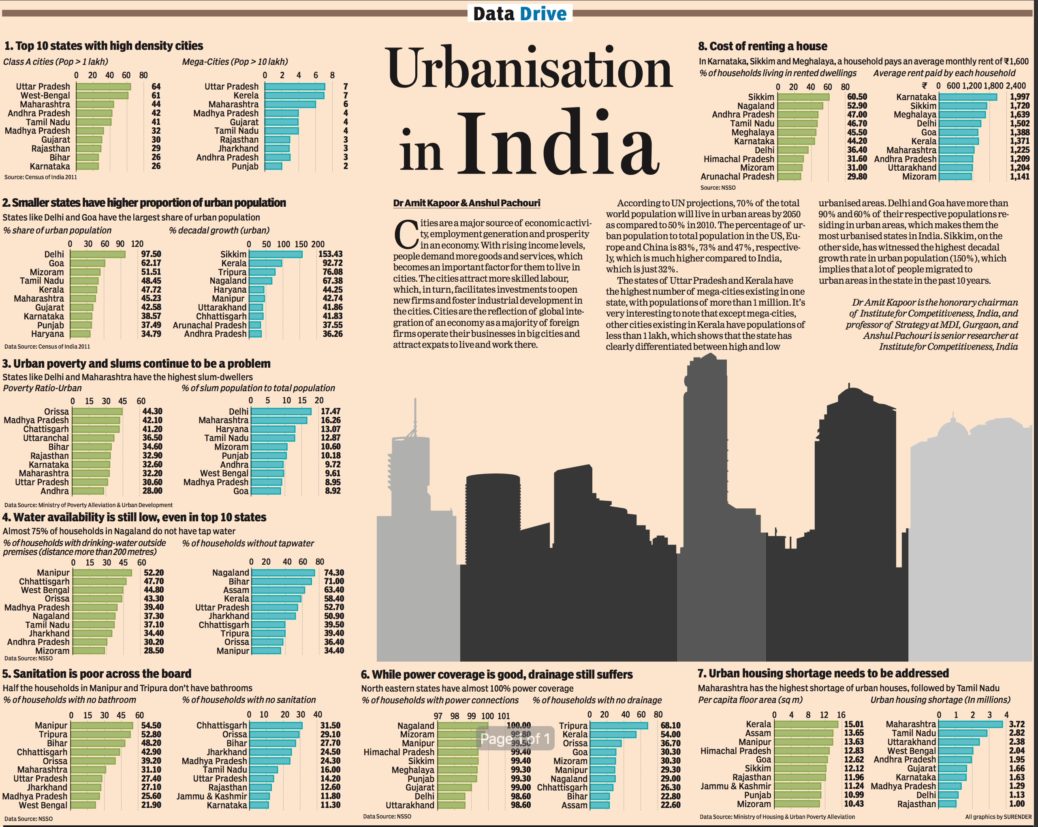
Cities are a major source of economic activity, employment generation and prosperity in an economy. With rising income levels, people demand more goods and services, which becomes an important factor for them to live in cities. The cities attract more skilled labour, which, in turn, facilitates investments to open new firms and foster industrial development in the cities. Cities are the reflection of global integration of an economy as a majority of foreign firms operate their businesses in big cities and attract expats to live and work there.
According to UN projections, 70% of the total world population will live in urban areas by 2050 as compared to 50% in 2010. The percentage of urban population to total population in the US, Europe and China is 83%, 73% and 47%, respectively, which is much higher compared to India, which is just 32%.
The states of Uttar Pradesh and Kerala have the highest number of mega-cities existing in one state, with populations of more than 1 million. It’s very interesting to note that except mega-cities, other cities existing in Kerala have populations of less than 1 lakh, which shows that the state has clearly differentiated between high and low urbanised areas. Delhi and Goa have more than 90% and 60% of their respective populations residing in urban areas, which makes them the most urbanised states in India. Sikkim, on the other side, has witnessed the highest decadal growth rate in urban population (150%), which implies that a lot of people migrated to urban areas in the state in the past 10 years.
This piece was published with Financial Express on January 28, 2012.